
r is known as the common ratio of the sequence. the first 20 odd numbers).Ī geometric progression is a sequence where each term is r times larger than the previous term. Sum the first 20 terms of the sequence: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9. You may need to be able to prove this formula. The sum to n terms of an arithmetic progression U n = 3 + 2(n - 1) = 2n + 1, which we already knew.
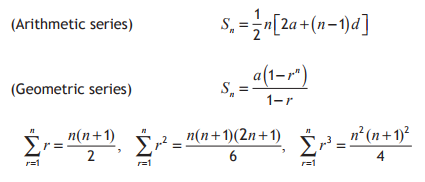
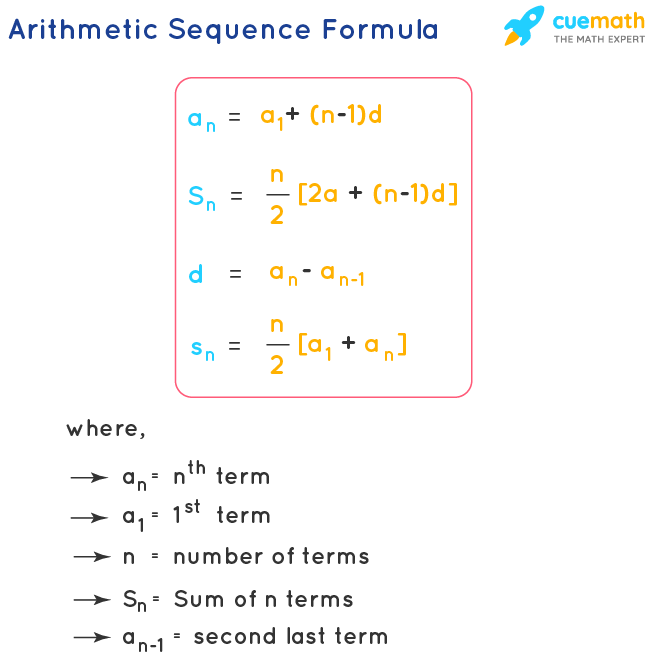
In general, the nth term of an arithmetic progression, with first term a and common difference d, is: a + (n - 1)d. The terms in the sequence are said to increase by a common difference, d.įor example: 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, is an arithmetic progression where d = 2. In the above example, U r = 3r + 2 and n = 3.Īn arithmetic progression is a sequence where each term is a certain number larger than the previous term. up to and including n in turn for r in U r. For the sequence U r, this means the sum of the terms obtained by substituting in 1, 2, 3. Now add up all of the term that you have written down. Keep doing this until you get to 4, since this is the number above the S. Then replace r by 2 and write down what you get. This means replace the r in the expression by 1 and write down what you get. The Greek capital sigma, written S, is usually used to represent the sum of a sequence. , the sum to 3 terms = S 3 = 2 + 4 + 6 = 12. The series of a sequence is the sum of the sequence to a certain number of terms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
